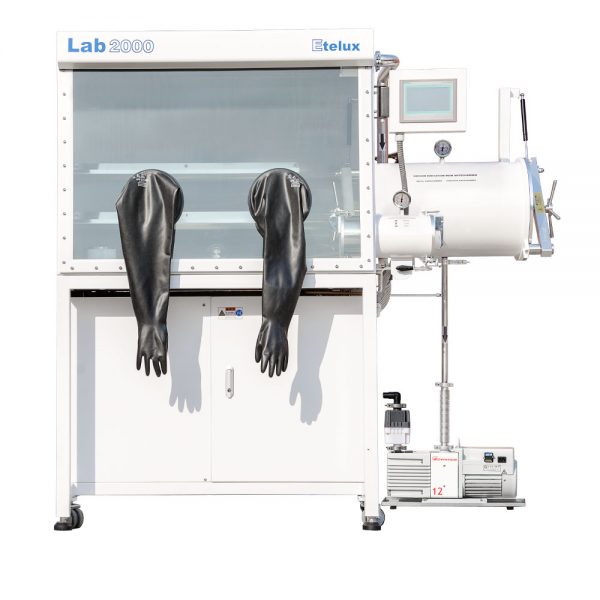
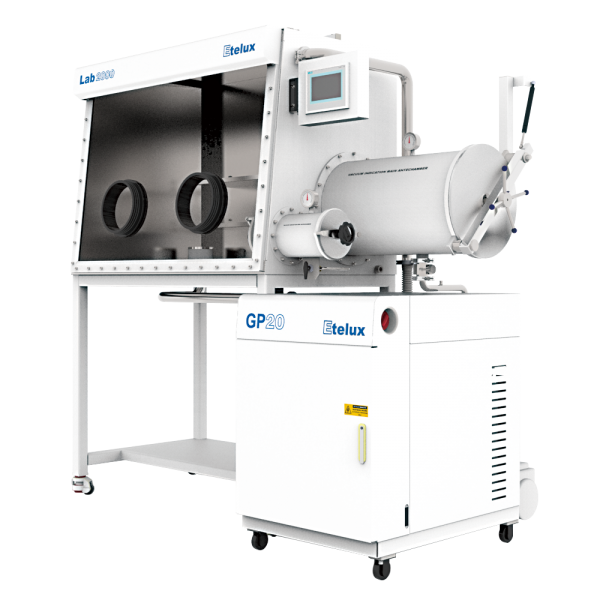
A high-temperature sintering furnace is a device for heating and sintering materials, usually widely used in industrial manufacturing and research. Its main function is to sinter powdered or granular materials into a dense solid structure through high temperature treatment, thus improving the mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, thermal stability and other properties of the material.Email:amy@etelux.com.
Main components
Furnace body:
Material: usually high temperature resistant materials, such as stainless steel, aluminum oxide, etc.
Structure: Includes a number of parts such as furnace shell, insulation layer and heating chamber.
Heating system:
Resistance heating: direct heating through resistance wire or electric heating element.
Induction heating: eddy current heating by electromagnetic induction.
Microwave heating: heating by utilizing microwave energy, applicable to specific materials.
Control system:
Temperature controller: accurately monitors and regulates the temperature inside the furnace.
Program Controller: Multiple heating curves can be set to realize complex sintering process.
Safety protection devices: such as overheating protection, power failure protection, etc.
Atmosphere control system (optional)
Inert gas protection: to prevent material oxidation.
Reduction atmosphere: for the reduction process of special materials.
Working Principle
The working principle of high temperature sintering furnace can be basically divided into the following processes:
Charging:
The material to be sintered is placed into the working chamber of the sintering furnace, usually on a high-temperature-resistant crucible or pallet.
Heating:
The temperature is raised to the desired sintering temperature, usually between 1000°C and 3000°C, by means of a heating system according to a set temperature profile.
Holding:
After the target temperature has been reached, it is held at that temperature for a period of time to ensure that the material is fully sintered. This phase may last several hours or even days, depending on the material and application requirements.
Cooling:
The rate of cooling is controlled so that the material cools gradually to avoid cracking or distortion caused by thermal stresses.
Application Areas
Ceramic Materials:
Preparation of high-strength ceramic components such as bearings, cutting tools, electronic packaging materials, etc.
Metal Materials:
Sintering metal powders to produce high performance alloys and composites.
Semiconductor Industry:
Used in crystal growth and doping process.
New energy field:
Manufacture of key components for fuel cells and lithium batteries.
Advantages and Features
High temperature stability: able to provide extremely high temperature to meet the sintering needs of different materials.
Precise temperature control: Through advanced control system, it realizes precise regulation of temperature.
Versatility: Compatible with a variety of heating methods and atmosphere control, applicable to a variety of sintering processes.
High-temperature sintering furnace plays an indispensable role in modern industry and scientific research, and its efficient and stable performance significantly improves the quality and efficiency of material manufacturing.