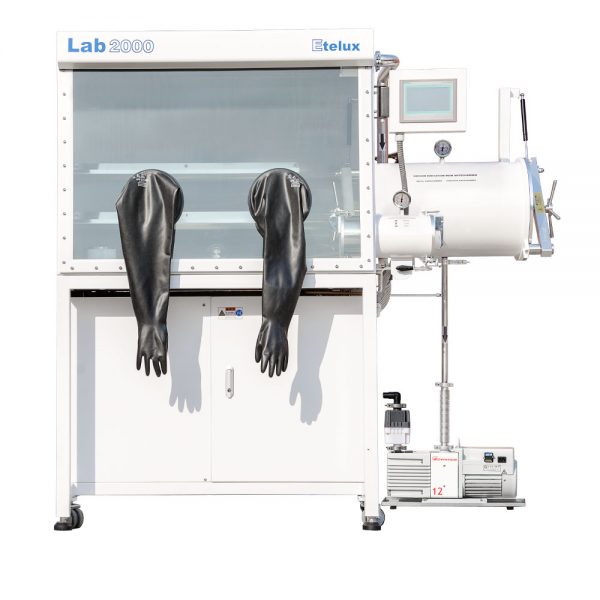
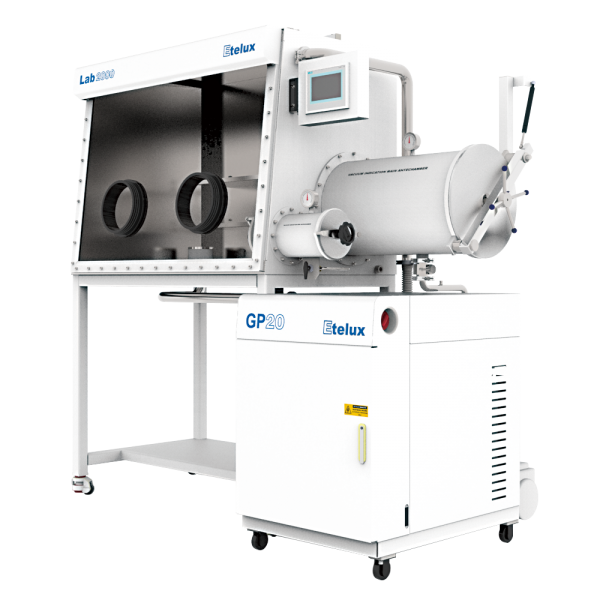
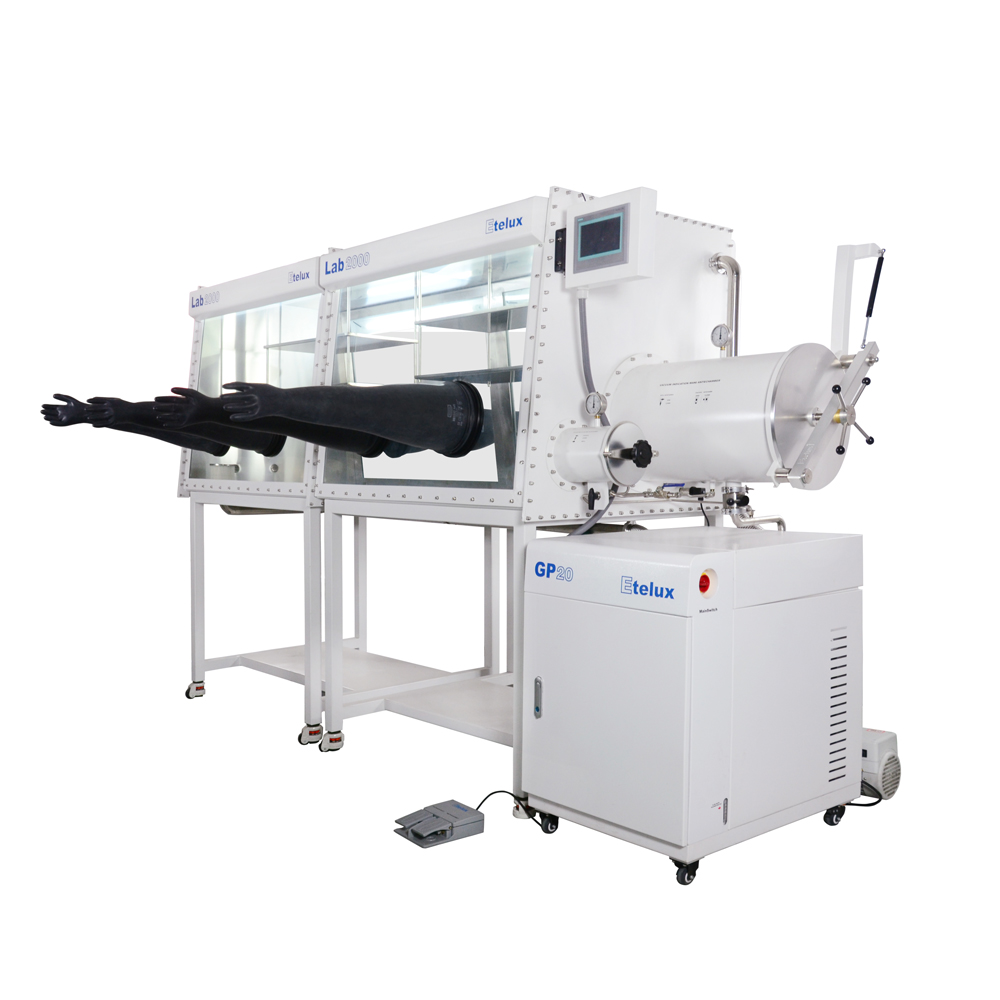
Inert gas gloveboxes are also known by a number of less descriptive names, including dry boxes, inert boxes, nitrogen boxes, low oxygen and/or humidity boxes, hypoxia boxes and anaerobic boxes.
Chambers, hypoxia and/or humidity chambers, oxygen deficiency chambers, and anaerobic chambers. All of these gloveboxes have one thing in common: they are usually hermetically sealed enough to allow some degree of control over the internal gas environment through a series of valves connected to the purified gas.
For a controlled atmosphere glovebox to function properly, the internal ambient gas in the
internal ambient gas contaminants must be removed and replaced with alternative or purified gases.
or purified gas. There are two methods of purging the box. In a constant purge system, a constant flow of inert gas is required. In gloveboxes where the evacuation/re-inflation method is used in the glovebox, a positive gas pressure and a negative vacuum can evacuate the main chamber of the glovebox and then refill it with inert gas.
The following is a detailed description of the working principle of an inert gas glove box, which will be divided into several main sections to ensure a full explanation.
- General
An inert gas glovebox usually consists of a sealed main chamber and two gloves, which are connected to the main chamber to enable the operator to operate in a closed environment through the gloves. The main chamber is usually filled with one or more inert gases, such as nitrogen or argon, to provide an oxygen-free, water-free environment. - Sealing system
The sealing system of an inert gas glove box is one of the key parts of its operation. The box is usually made of impermeable materials such as stainless steel or polymer materials and special sealing techniques are used to ensure that the gas does not escape. This can be achieved through the use of O-rings, vacuum seals and high quality door and glove connections. - Inert gas environment
Inert gases are gases that do not readily react chemically with other elements or compounds. Commonly used inert gases in inert gas gloveboxes include nitrogen (N2) and argon (Ar). The choice of these gases depends on the requirements of the particular experiment and the properties of the material. - Operating Gloves
Gloves are the primary means by which the operator interacts with the interior of the glove box. These gloves are usually made of soft, chemical-resistant materials such as vinylized polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or nitrile rubber. The gloves are attached to the box by a seal to ensure that the internal environment is protected from outside contamination. - Gas circulation and handling
Inert gas gloveboxes are usually equipped with gas circulation and treatment systems to ensure the quality and purity of the gas inside the box. These systems include gas circulation pumps, gas filters and humidity controls to remove impurities from the chamber, maintain a constant gas pressure and maintain the required humidity level. - Applications
Inert gas gloveboxes are used in a wide range of applications such as chemical synthesis, catalyst preparation, materials science, and battery development. Its main benefits include protecting materials from reactions such as air oxidation and hydrolysis, as well as providing a controlled operating environment to ensure accuracy and reproducibility of experiments. - Safety Precautions
When using an inert gas glove box, operators need to pay attention to some safety precautions, such as checking the sealing system regularly, avoiding contact with sharp objects inside the glove box to prevent perforated gloves, and handling toxic or flammable materials properly.